The Egyptian Society for Blood Transfusion Services
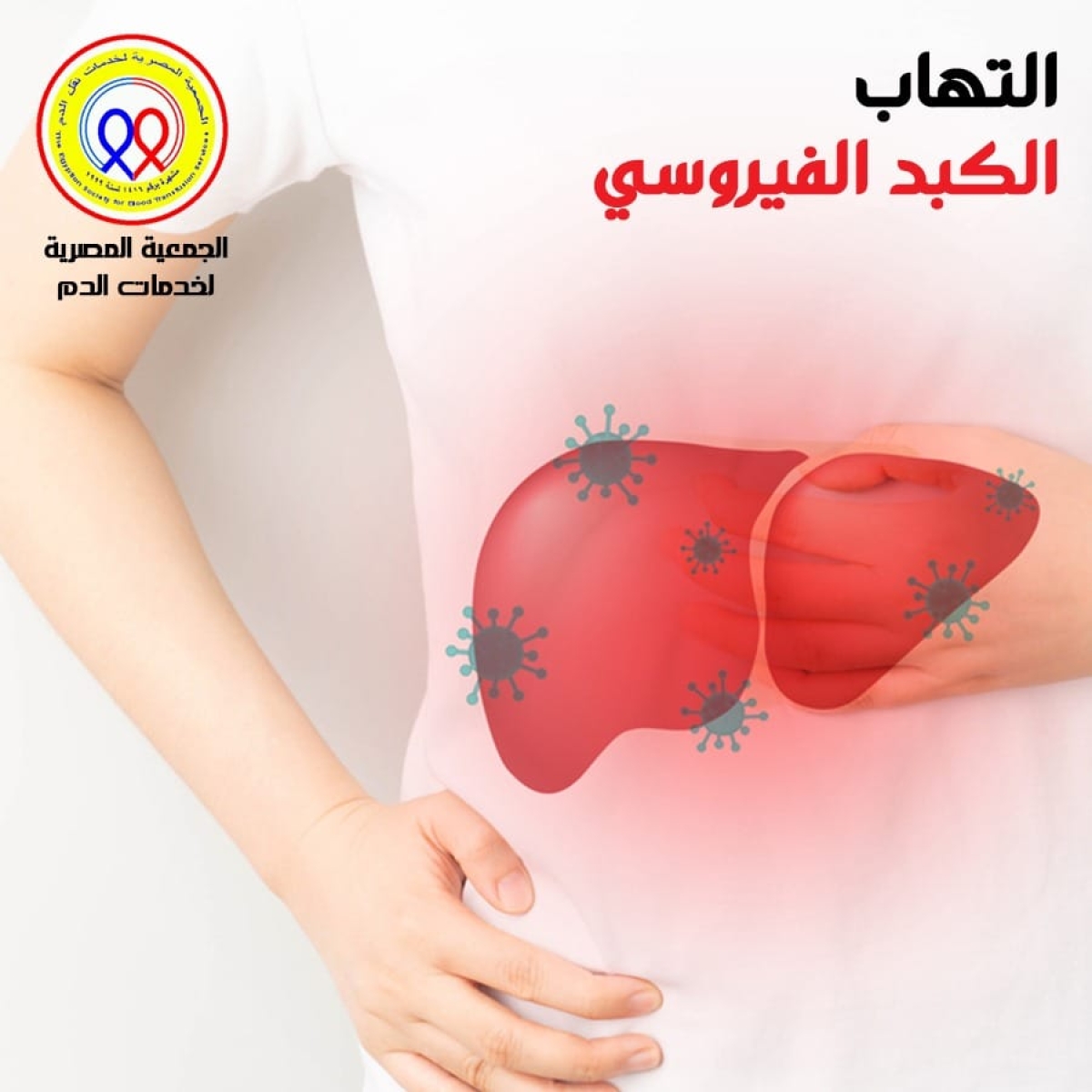
Viral hepatitis is an inflammatory condition of the liver tissue as a result of a viral infection.
Types of viral hepatitis There are several different types of viral hepatitis, and they are as follows:
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis b.
Hepatitis c.
Hepatitis d.
Hepatitis D virus appears only in people who have previously been exposed to the type B virus.
In order to reduce the risk of exposure to the virus as a result of a transfusion of infected blood, hospitals perform tests
And several tests in order to rule out the possibility of the presence of the virus in the blood meals provided to patients, and the probability of infection with hepatitis C virus type is 1: 100,000.
Symptoms of viral hepatitis Hepatitis A is a relatively mild disease and its symptoms do not last for a long time, but long-term hepatitis B, lupus-like hepatitis C, and type D lead to long-term symptoms that require long and continuous medical treatment., Symptoms of hepatitis
Viral diseases are multiple and related to the cause of the disease and the degree of damage to the liver. In relatively easy cases, the disease is asymptomatic, or with symptoms similar to those of mild influenza:
High body temperature.
A feeling of exhaustion and general fatigue.
Anorexia.
Nausea and vomiting.
Discomfort and pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, as a result of swelling and enlargement of the liver.
muscle pain;
1. Serious symptoms of hepatitis C. In more severe cases of viral hepatitis, because the liver is damaged and unable to filter the blood effectively, toxic chemicals build up in the circulation, causing the following symptoms:
Yellowing of the skin and the white part of the eyes.
Concentrated and dark urine.
A turd that tends to be gray in color.
High temperature and a general feeling of illness.
This condition is life threatening and requires immediate medical treatment, otherwise the damage to the liver is irreversible.
Ways of infection: Viral hepatitis infection can be transmitted from one person to another in several different ways, depending on the virus responsible for the disease, such as:
Contact with the feces of a person infected with hepatitis A virus.
Eating seafood infected with sewage contaminated with hepatitis A virus.
Contact with infected blood, vaginal secretions, semen, and breast milk contaminated with hepatitis B virus.
Having unprotected sexual relations with a person infected with the hepatitis virus of two types: type B and type C.
Use of used or contaminated syringes with hepatitis B, C, or D.
Risk factors. Hepatitis may be caused by various etiological factors, such as:
Excessive consumption of alcohol.
Some drug treatments.
Herpes simplex virus.
A bacterial infection that can cause hepatitis.
Complications of viral hepatitis Among the most important complications of viral hepatitis are:
Cirrhosis.
Chronic hepatitis.
liver failure.
Prevention of viral hepatitis To prevent infection with viral hepatitis, you must follow the following:Receiving vaccinations for hepatitis A and type B.
Practice safe sex by using a condom.
Not using the injured person's tools.
Do not share syringes with others.
Maintain personal hygiene.